Civil Service Educator
A Civil Service Educator is a teacher, mentor, or coach who specializes in preparing aspirants for Civil Services Examinations (such as the UPSC CSE in India, the Civil Service Fast Stream in the UK, or similar public administration exams globally).
While the term can technically refer to a government teacher (a “civil servant” who is an “educator”), in the context of your previous request, it almost certainly refers to someone who trains future officers.
The National Education Policy states that there should be one teacher (Civil Service Educator) for every 30 students in India. However, the actual situation in the country is quite different.
Statistics show that millions of teaching positions are vacant. Large-scale recruitment drives for these positions are also conducted every year or two.
This means that there is a need for teachers (Civil Service Educator) in the country, and this presents an opportunity for you. You just need to know the right path and qualifications.
It is generally believed that a Bachelor of Education (B.Ed.) degree is necessary to become a teacher in India.
There are so many courses that can lead to teaching jobs.
Civil Service Educator
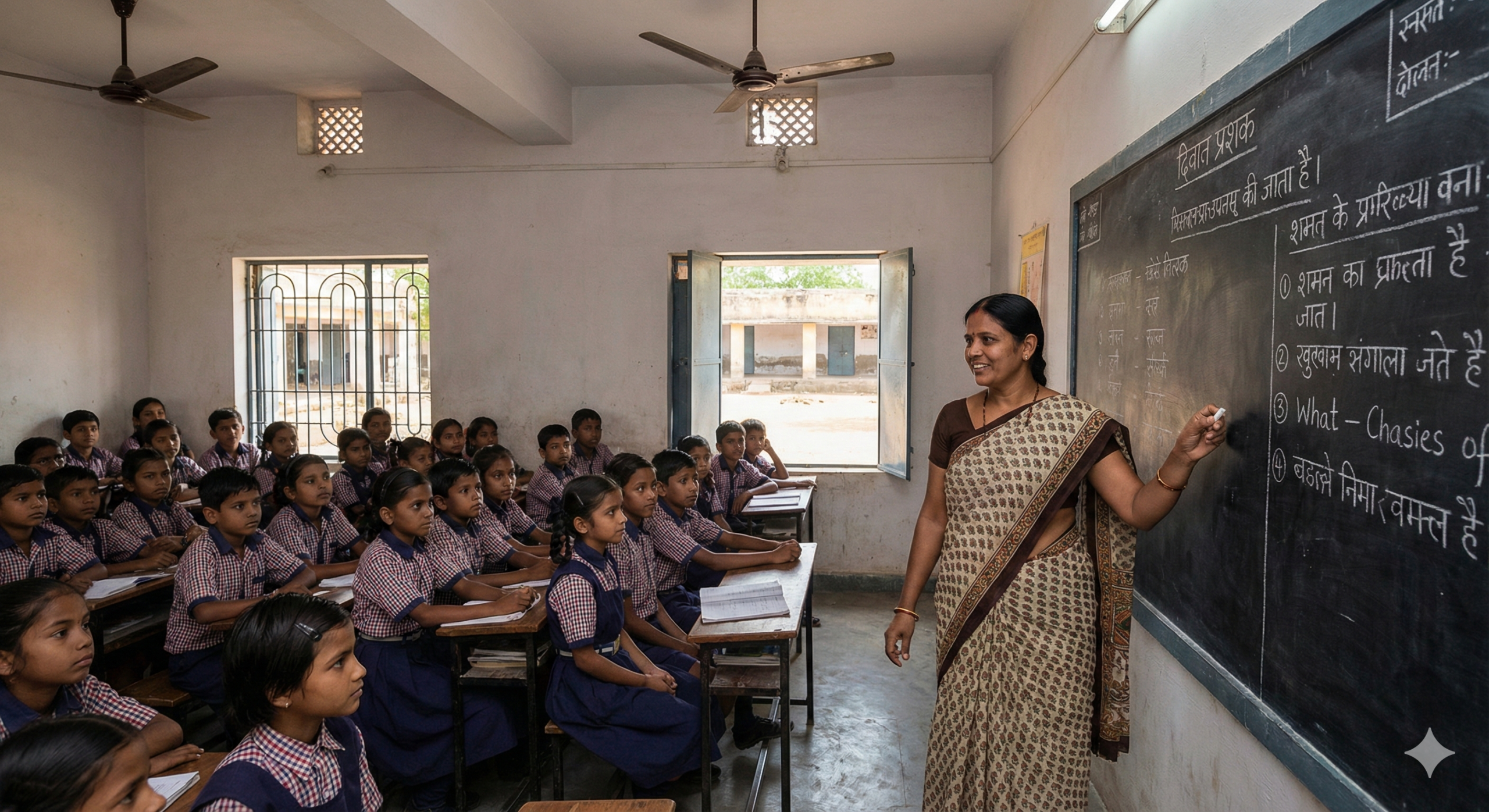
Civil Service Educator
UP police requirement 2025
How is becoming a Civil Service Educator the right choice?
Sachin, a primary school teacher (Civil Service Educator) at a Delhi Municipal Corporation school, has been teaching children for the past fifteen years. Besides his work at the school, he also guides and mentors underprivileged individuals who want to pursue a career in teaching.
When asked why he chose this profession, he says, “If you want to bring about change, start from the roots. If you work with the foundations, even if it takes time, the change that comes will be the kind you desire.”
Saurav, who prepares students for the Teacher Eligibility Test (TET), a mandatory qualification exam for teachers, says that the literacy rate in the country is increasing, new educational institutions are opening every day, and the government is also taking several initiatives to strengthen the education sector. As a result, the demand for teachers is also increasing rapidly.
Both agree that teaching is a profession that offers a stable career.
“A job in a private school can be a bit risky because it depends on the type of school, the number of students, and the overall environment. But a government job offers stability along with a good salary. The starting salary for a six-hour workday is around 50,000 rupees. There are opportunities for promotion, and a good work-life balance.”Said by gaurav.
Himanshi Singh comes from a family of teachers and herself prepares students for teacher recruitment exams.
She says, “There are millions of vacant teaching positions in the country. The government’s investment in education has increased, and a new education policy has been introduced. At the same time, the demand for qualified teachers in schools and on ed-tech platforms has increased rapidly. Therefore, this is an opportune time to become a teacher.”
How many types of Civil Service Educator are there?
The paths to becoming a teacher (Civil Service Educator) vary depending on the candidate’s teaching level. For example:
Primary School Teacher (PRT): These teachers teach children from classes one to five.
Trained Graduate Teacher (TGT): These teachers teach children from classes six to eight.
Post Graduate Teacher (PGT): These teachers teach senior secondary classes, i.e., classes eleven and twelve.
There are also necessary educational qualifications for these positions.
Primary Teacher: Must have passed 12th grade + D.El.Ed/Junior Basic Training or a four-year B.El.Ed (Bachelor of Elementary Education) degree after 12th grade.
TGT: Graduation with B.Ed is mandatory.
PGT: Post-graduation in the relevant subject + B.Ed is required.
Now, for candidates who want to apply for vacancies in these positions, a basic requirement is that they must also clear the Central or State Teacher Eligibility Test, i.e., CTET or STET.
Himanshi Singh explains that the rules for recruiting teachers in private schools are also similar, especially in large and reputable private schools.
For instance, it is mandatory for applicants for any vacancy to have cleared the CTET or TET. They must also have a graduation/post-graduation degree in the relevant subjects along with a B.Ed/B.El.Ed degree. These schools usually advertise vacancies on their websites, job portals, etc., where the complete application process is also described.
These exams are essential for being a Civil Service Educator
TETs are exams that don’t guarantee a job, but you can’t get a government job without clearing them.
The most important is the CTET, or Central Teacher Eligibility Test. these exams are conducted by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE).
This exam is considered difficult because experts say its qualification rate is only 14-15 percent.
This is a national-level examination that qualifies candidates to become teachers in central government schools such as Kendriya Vidyalayas, Navodaya Vidyalayas, or schools in Union Territories.
Similar to the CTET, many states also conduct eligibility tests for teachers (Civil Service Educator). For example:
UPTET (Uttar Pradesh)
HTET (Haryana)
MAHA TET (Maharashtra)
REET (Rajasthan)
TNTET (Tamil Nadu)
WBTET (West Bengal)
KARTET (Karnataka)
OTET (Odisha)
TSTET (Telangana)
APTET (Andhra Pradesh)
Assam TET (Assam)
PSTET (Punjab)
Candidates who pass these exams become eligible to apply for government teaching positions.
The respective state recruitment boards then release vacancies according to their needs, and candidates can finally get a job by clearing the different levels of the state recruitment board examinations.
However, the Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan and Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti conduct separate examinations for the recruitment of their teaching staff across India. The Delhi Subordinate Services Selection Board also conducts separate recruitment for teachers in schools under the Delhi government.
Essential Courses for Teaching(Civil Service Educator)
After completing 12th grade, any candidate can choose from various teaching-related courses, whether it’s a graduation program, a diploma, or an integrated degree program. All these courses are also essential for teaching in private schools.
B.Ed: This is a two-year course after graduation that prepares candidates to become teachers at different levels. However, some colleges also offer a four-year integrated B.Ed program along with graduation, where both graduation and Bachelor of Education are completed together.
ITEP: Under the National Education Policy, a new program has been introduced: the Integrated Teacher Education Program. This course has started at Delhi University, Jamia Millia Islamia, and BR Ambedkar University. Students pursuing this program complete their graduation and B.Ed simultaneously. The advantage is that the course is completed in four years instead of five.
B.El.Ed: Bachelor of Elementary Education. This is also a four-year undergraduate teacher training program that includes subjects like psychology, pedagogy, and practical teaching skills.
D.El.Ed: Diploma in Elementary Education. This is a two-year diploma program designed to train teachers for the primary and upper-primary levels.
Its syllabus includes subjects like child development, pedagogy, and practical classroom training, enabling teachers to teach children from grades one to five. In simple terms, pedagogy is the subject related to the methods and practices of teaching.
D.Ed: Diploma in Education is also a two-year teacher training program designed to train teachers for all subjects from grades one to eight.
NTT: Nursery Teacher Training is a two-year specialized diploma certification program for those who want to become teachers at the nursery and pre-school levels.
Saurav says that while B.Ed is a popular route, one can also enter private institutions based on diplomas or certificates by choosing courses like pre-primary, special education, and skill-based teaching.
What should be the exam preparation strategy?
First, understand the exam pattern. Exams like TET or CTET have two papers. Paper One is for those who want to teach classes one to five, and Paper Two is for those who want to teach classes six to eight.
Each paper consists of multiple-choice questions (MCQs) covering subjects such as Child Development and Pedagogy, Language, Mathematics, Environmental Studies, and Social Studies.
But how to prepare for it? Sachin explains, “The first source is NCERT books, which are essential for basic concepts. For general knowledge, Lucent’s book, for English, Chetan anand’s ‘English is Easy,’ and for Hindi, Manak Hindi Vyakaran are quite helpful.”
“Besides this, solving previous years’ exam questions helps you understand the type of questions asked. Now, free online content is readily available, so students don’t face any difficulties, and many are becoming teachers with its help. However, studying from books and then taking the exam is my personal preference.”
Regarding how much time a student might need for preparation, Himanshi Singh says, “Students should keep taking mock tests and assess their preparation by identifying areas where they need improvement. They should also pay attention to how much time they are taking to solve the questions. If you can do all this in three months, then three months are sufficient for preparation.”
Saurav says, “The preparation strategy should be simple but consistent. Clarity of content, understanding of pedagogy, and regular practice are essential for TET preparation.”
It’s also important to keep these things in mind for being a Civil Service Educator (Teacher):
Every course, such as B.Ed and B.El.Ed, is accredited by the NCTE (National Council for Teacher Education).
Sometimes, students pursue these courses from private institutions. Therefore, experts advise that when choosing any course, students should ensure that the course is approved by the NCTE.
Saurav says that you should ensure that the course curriculum is updated, the practical training is of good quality (i.e., the quality of teaching practice), the internship school is reputable, and that the course adheres to NCTE guidelines.
Civil Service Educator
RELATED POSTS
View all